Introduction
PCBAs work in conjunction with components through circuit connections to realize the functions of electronic devices, forming the core of modern electronic products. They not only provide current paths but also undertake tasks such as signal transmission, power management, and safety protection.

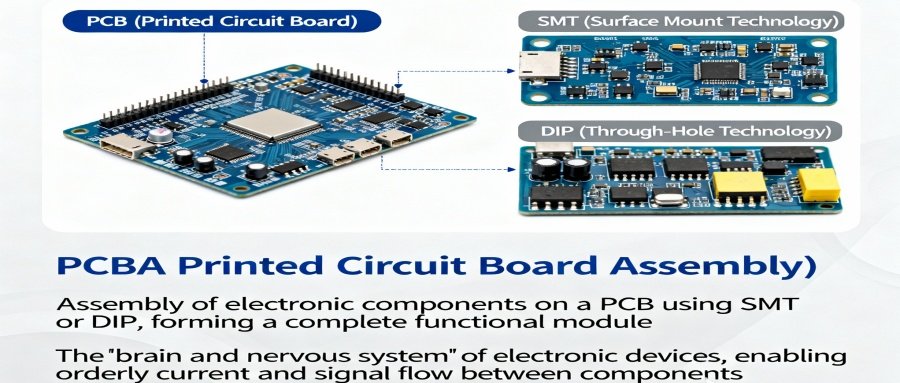
What is a PCBA?
A PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) refers to the assembly of electronic components on a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) using surface mount technology (SMT) or through-hole technology (DIP), forming a complete functional module. It is the “brain and nervous system” of electronic devices, allowing current and signals to flow orderly between components.
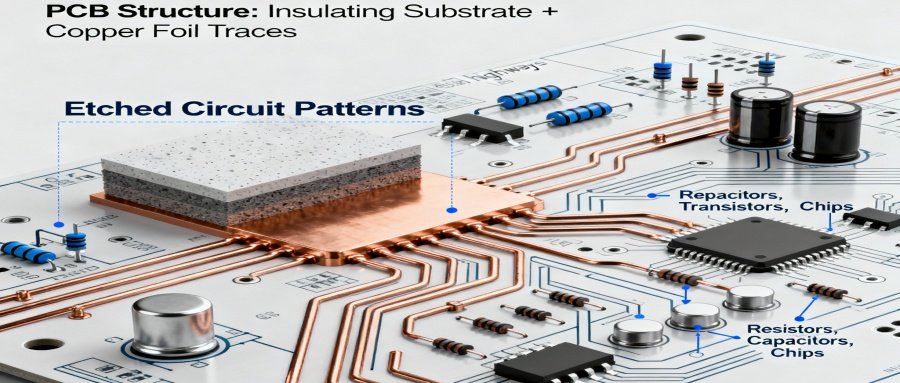
Circuit Network Construction
- A PCB consists of an insulating substrate and copper foil traces.
- The copper foil is etched to form specific circuit patterns.
- These traces act like “electronic highways,” connecting components such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and chips to form a complete circuit network.
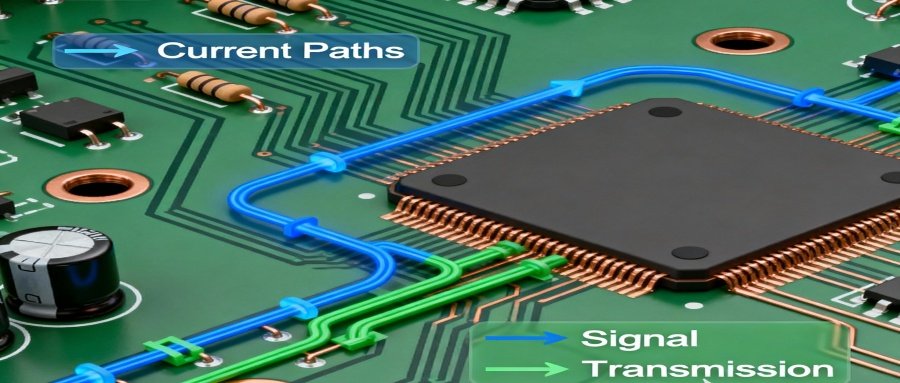
Current Paths and Signal Transmission
- When power is applied, current flows along the conductive traces on the PCB, driving the components to operate.
- Signal traces are responsible for transmitting control and data signals, enabling information exchange.
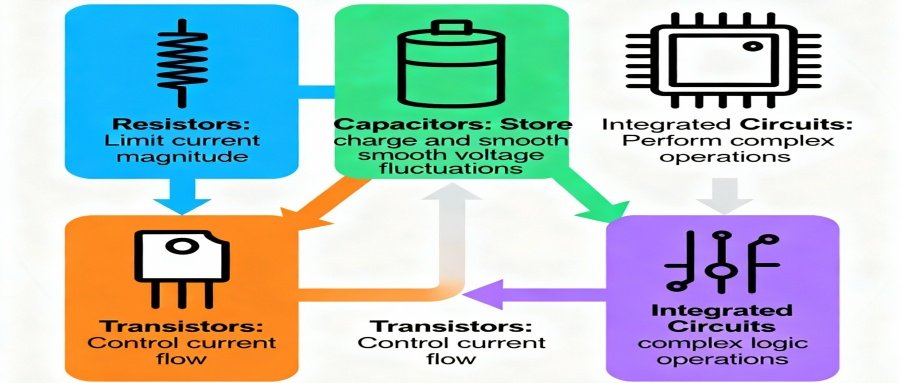
Synergistic Effect of Components
- Resistors: Limit current magnitude
- Capacitors: Store charge and smooth voltage fluctuations
- Transistors: Control current flow
- Integrated Circuits: Perform complex logic operations
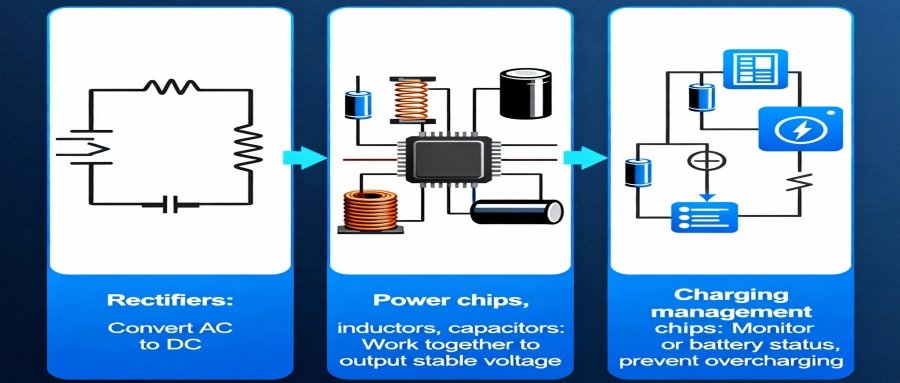
Power Management and Energy Conversion
- Rectifiers convert AC to DC.
- Power chips, inductors, and capacitors work together to output a stable voltage.
- Charging management chips monitor battery status and prevent overcharging.
Protection and Safety Mechanisms
- Fuses: Blow when overloaded to protect the circuit.
- Overcurrent Protection: Automatically cuts off when current is too high.
- Overheat Protection: Triggers an alarm or shuts down when temperature is too high.

Applications of PCBAs
New Energy: Battery management systems, charging stations
Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, computers, tablets, TVs
Automotive Electronics: Vehicle control systems, navigation, power management
Medical Equipment: Patient monitors, diagnostic instruments
Industrial Control: Automation equipment, IoT terminals




