Introduction
In today’s fast-paced electronics industry, efficiency and reliability are the cornerstones of competitiveness. Terms like pcb, smt and pcba are not just technical jargon — they represent critical stages in the value chain that directly impact product quality, cost, and time-to-market. For manufacturers, suppliers, and clients, understanding these concepts is key to making informed business decisions.

PCB: The Foundation of Electronic Products
- Business Role: PCBs are the backbone of all electronic devices, from smartphones to industrial machinery.
- Commercial Value: High-quality PCBs reduce failure rates, enhance durability, and build customer trust.
- Market Impact: PCB design innovation (multi-layer, flexible boards) enables companies to differentiate products and enter new markets such as wearables or automotive electronics.

SMT: Driving Efficiency in Manufacturing
- Business Role: SMT is the assembly technology that allows miniaturization and high-speed production.
- Commercial Value:
- Reduces labor costs through automation.
- Enables compact designs, meeting consumer demand for smaller, lighter devices.
- Improves production scalability, vital for mass-market electronics.
- Market Impact: SMT adoption is a competitive advantage, allowing companies to deliver faster, cheaper, and more reliable products.
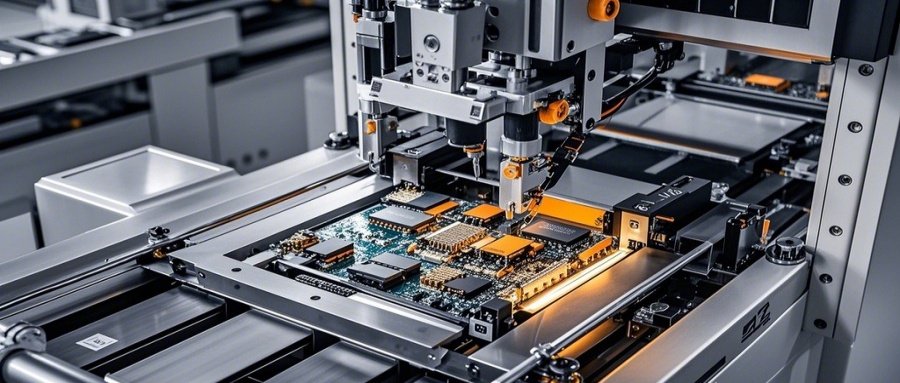
PCBA: The Market-Ready Product
- Business Role: PCBA represents the finished, functional board ready for integration into end products.
- Commercial Value:
- Directly determines product performance and customer satisfaction.
- Quality PCBA reduces warranty claims and strengthens brand reputation.
- Market Impact: PCBA suppliers are critical partners in the electronics supply chain, often serving as the link between design houses and consumer brands.

Differences and Business Connections
| Term | Business Meaning | Value Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| PCB | Bare board | Foundation for innovation and reliability |
| SMT | Assembly process | Efficiency, cost reduction, scalability |
| PCBA | Assembled board | Market-ready product, customer satisfaction |
- Differences: PCB is the raw material, SMT is the process, PCBA is the finished product.
- Connections: Together, they form a seamless chain — from design to production to market delivery.

Conclusion
👉 txjpcba.com For businesses in the electronics sector, PCB, SMT, and PCBA are not isolated concepts but interconnected pillars of success. A strong PCB design, efficient SMT process, and reliable PCBA output translate into competitive products, reduced costs, and faster time-to-market. Companies that master this chain position themselves as leaders in innovation and customer trust.






